How to Make a P&L Statement: Simple Guide
Have you ever wondered how businesses keep track of their financial health?
Enter the Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, a crucial financial document that provides a snapshot of a company's financial performance over a specific period.
Whether you're a small business owner or an aspiring entrepreneur, understanding how to create and interpret a P&L statement is essential for making informed business decisions.
In this guide, we'll walk you through the process of making a P&L statement, breaking down each component and providing step-by-step instructions.
By the end, you'll have the knowledge to create your own P&L statement and use it to drive your business forward.
Components of a P&L Statement
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of creating a P&L statement, let's explore its key components. Understanding these elements will help you grasp the bigger picture of your business's financial performance.
Revenue
Revenue is the lifeblood of any business. It's the total amount of money earned from selling goods or services during a specific period. But did you know there are different types of revenue?
- Operating Revenue: This is the income generated from your primary business activities.
- Non-Operating Revenue: Think of this as the "bonus" income, such as interest earned on investments or proceeds from selling assets.
To calculate total revenue, simply add up all the money your business has earned during the period in question. For example, if you sold $50,000 worth of products and earned $2,000 in interest, your total revenue would be $52,000.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing or purchasing the goods you sell. It's like the ingredients in a recipe - you can't make the final product without them.
Calculating COGS involves adding up costs such as:
- Raw materials
- Direct labor
- Manufacturing overhead
For a retail business, COGS might simply be the cost of purchasing inventory for resale.
Gross Profit
Gross profit is what's left after subtracting COGS from your total revenue. It's like the first checkpoint in your profitability journey. To calculate gross profit:
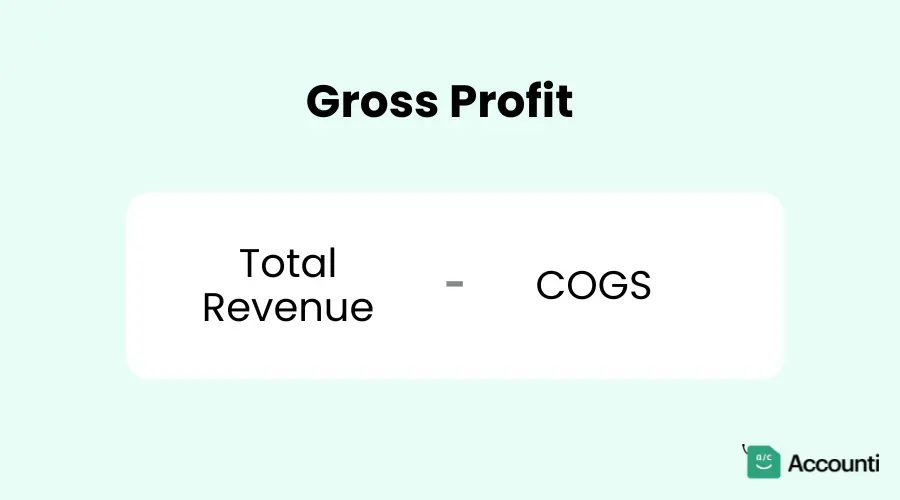
This figure gives you a clear picture of how much money you're making from your core business activities before accounting for other expenses.
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses are the costs incurred in the day-to-day running of your business. They can be divided into two main categories:
- Fixed Costs: These remain constant regardless of your sales volume. Examples include rent, insurance, and salaries.
- Variable Costs: These fluctuate based on your business activity. Think of advertising expenses, utilities, and shipping costs.
Understanding the difference between fixed and variable costs can help you make smarter decisions about scaling your business or cutting expenses when needed.
Operating Profit
Operating profit, also known as Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT), shows how much your business is making from its core operations. To calculate operating profit:

This figure gives you insight into your business's efficiency and profitability before accounting for non-operating items.
Non-Operating Income and Expenses
Non-operating items are those not directly related to your core business activities. They can include:
- Interest income or expenses
- Gains or losses from selling assets
- One-time expenses or windfalls
While these items aren't part of your regular business operations, they still impact your overall profitability.
Net Profit (or Loss)
Net profit is the bottom line - literally! It's what's left after accounting for all revenues, expenses, and non-operating items. To calculate net profit:
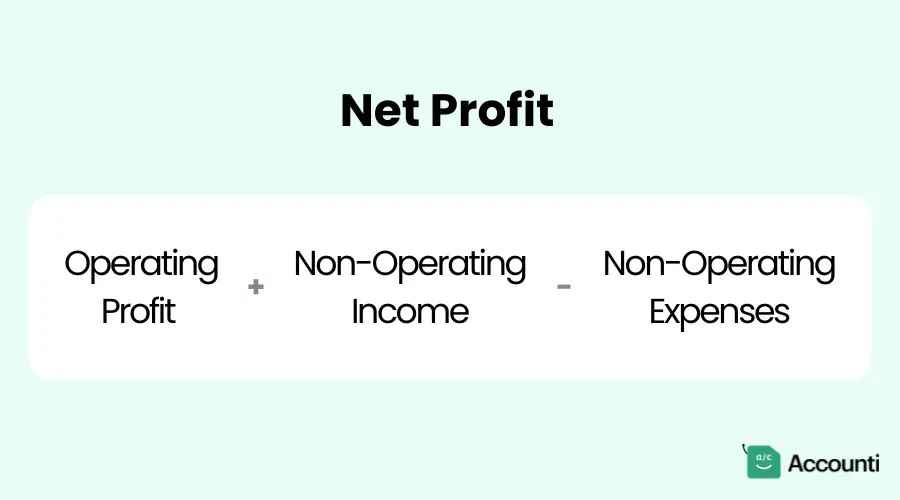
If this number is positive, congratulations! Your business is profitable. If it's negative, you've incurred a net loss for the period.
Steps to Create a P&L Statement
Now that we've covered the components, let's walk through the process of creating a P&L statement. Don't worry, it's not as daunting as it might seem!
Step 1: Collect Financial Data
The first step in creating an accurate P&L statement is gathering all your financial data. This includes:
- Sales records
- Expense receipts
- Bank statements
- Payroll information
Remember, the accuracy of your P&L statement depends on the quality of your data. It's like baking a cake - use the wrong ingredients, and the end result won't be what you expected.
Step 2: Organize Revenue and Expenses
Once you have all your financial data, it's time to organize it. Group your income and expenses into categories that make sense for your business. For example:
- Revenue categories: Product sales, service fees, interest income
- Expense categories: Inventory costs, wages, rent, utilities, marketing
Think of this step as sorting your laundry - it's much easier to deal with when everything's in its proper place.
Step 3: Calculate Gross Profit
Now that your revenue and COGS are organized, you can calculate your gross profit:
- Add up all your revenue for the period.
- Sum up your total COGS.
- Subtract COGS from revenue.
Voila! You've got your gross profit. This figure tells you how much money you're making on your products or services before accounting for other expenses.
Step 4: Subtract Operating Expenses
Next, it's time to account for your operating expenses:
- List all your operating expenses.
- Add them up to get your total operating expenses.
- Subtract this total from your gross profit.
The result is your operating profit. This shows how much your business is making from its core activities.
Step 5: Include Non-Operating Items
Don't forget about those non-operating items we discussed earlier:
- List any non-operating income (like interest earned).
- List any non-operating expenses (like interest paid on loans).
- Add non-operating income and subtract non-operating expenses from your operating profit.
Step 6: Calculate Net Profit (or Loss)
You're in the home stretch! After accounting for non-operating items, you'll arrive at your net profit (or loss). This final figure represents your business's overall profitability for the period.
Example of a P&L Statement
Let's put all this information into practice with a sample P&L statement:
|
Item |
Amount |
|
Revenue |
$100,000 |
|
Cost of Goods Sold |
$60,000 |
|
Gross Profit |
$40,000 |
|
Operating Expenses |
|
|
- Rent |
$5,000 |
|
- Utilities |
$2,000 |
|
- Salaries |
$15,000 |
|
- Marketing |
$3,000 |
|
Total Operating Expenses |
$25,000 |
|
Operating Profit |
$15,000 |
|
Non-Operating Income |
$1,000 |
|
Non-Operating Expenses |
$2,000 |
|
Net Profit |
$14,000 |
In this example, the business generated $100,000 in revenue, had $60,000 in COGS, resulting in a gross profit of $40,000. After subtracting operating expenses and accounting for non-operating items, the business ended up with a net profit of $14,000.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When creating your P&L statement, watch out for these common pitfalls:
- Overlooking small expenses: Even minor costs can add up over time. Don't forget to include things like office supplies or bank fees.
- Misclassifying costs: Make sure you're categorizing expenses correctly. For instance, don't confuse COGS with operating expenses.
- Not updating regularly: Your P&L statement should be a living document. Update it regularly to keep your finger on the pulse of your business.
Tips for Maintaining an Accurate P&L Statement
To ensure your P&L statement remains a reliable tool for decision-making, consider these tips:
- Use accounting software: Tools like QuickBooks, Zoho and Xero can automate much of the process and reduce errors.
- Regularly review and update financial records: Set aside time each week or month to update your books.
- Reconcile with bank statements: This helps catch any discrepancies and ensures all transactions are accounted for.
Conclusion
Creating and maintaining an accurate P&L statement is crucial for understanding your business's financial health and making informed decisions. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you'll be well-equipped to create your own P&L statement and use it to drive your business forward.
Remember, a P&L statement is more than just numbers on a page - it's a story of your business's performance. By regularly reviewing and analyzing your P&L statement, you can identify trends, spot potential issues before they become problems, and capitalize on opportunities for growth.
So, roll up your sleeves, gather your financial data, and start creating your P&L statement today. Your future self (and your business) will thank you!

 Rohit Kapoor
Rohit Kapoor

